Swiss chard Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Swiss chard is a green that is closely related to beets. Like other green leafy vegetables, it has highly nutritious leaves, making it a popular component of healthy diets. Swiss chard is the same species as beetroot. It is one of the hardier leafy greens, with a harvest season typically lasting longer than kale, spinach, or baby greens.
Chard goes by many names—Swiss chard, leaf beet, seakettle beet, and spinach beet, to name a few. It is a beautiful large-leaf vegetable with wide flat stems resembling celery. The leaf blade can be green or reddish in color; the leaf stalks are usually white, or a colorful yellow or red. The ruby variety is especially charming with its vivid red stem and broad dark green leaves. If you like spinach, you will adore chard. The flavor is mild yet earthy and sweet with slightly bitter undertones.
The nutritional value of Swiss chard
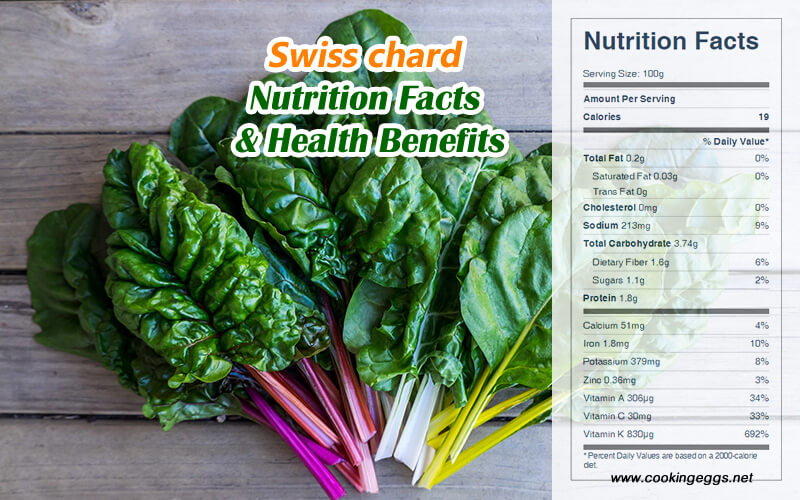
Raw Swiss chard is 93% water, 4% carbohydrates, and 1% protein, with negligible fat. They supply plenty of vitamins A, K, and C. It contains low amounts of carbohydrates, protein, fat, and dietary fiber.
One-half cup of boiled, chopped Swiss chard provides 18 calories, 3.6 g carbohydrate, 1.7 g protein, 0.1 g fat, 1.8 g dietary fiber, 2762 IU vitamin A, 16 mg vitamin C, 8 mcg folic acid, 483 mg potassium, 158 mg sodium, 29 mg phosphorus, 51 mg calcium, 2 mg iron, and 76 mg magnesium.
Raw Swiss chard Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Swiss chard
Swiss chard is very low in calories, fats, saturated fat and cholesterol, making it perfect for a weight loss diet. It also helps keep blood pressure down.
The same betacyanins and betaxanthins found in beets are found in Swiss chard. They may protect against oxidation of low-density lipoproteins.
Swiss chard also contains antioxidant phenols and flavonols, which have been shown in the laboratory to inhibit the growth of some types of cancer cells.
Swiss chard leaves are an excellent source of vitamin C (33% of the Daily Value per 100 g). As a powerful antioxidant, vitamin C helps remove free radicals and reactive oxygen species from the body through its reduction potential properties.
Swiss chard supplies large amounts of vitamin K (692% of the Daily Value per 100 g). Research suggests that deficiency of vitamin K may also weaken bones, potentially contributing to osteoporosis, and may promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.
It also provides the B vitamins B6, thiamine, niacin, and folic acid, and the minerals calcium, selenium, and zinc. It is a good source of carotenes and fiber.
Health Risk
Swiss chard does contain measurable amounts of oxalates, which can inhibit the absorption of calcium and iron, and so should be consumed only in moderation. So, over-consumption can cause problems for those with kidney disease, gout, vulvar pain, rheumatoid arthritis, or other conditions that may require a low-oxalate diet.
Swiss chard is very high in sodium.