Pine Nuts Nutrition Facts & Health Benefits
Pine nuts, also called pignoli or chilgoza, pine kernels are small edible seeds that are extracted from the pine cone of various species of pine.
There are more than 20 varieties of pine trees that produce an edible seed, and the nutritional value varies somewhat among them, but most pine nuts can be counted on to provide protein, fat, and the B vitamins thiamine, niacin, and riboflavin. They are also a source of magnesium, iron, and phosphorus. More than half of the carbohydrates in pine nuts are dietary fiber. Pine nuts also contain pinolenic acid, which appears to stimulate the production of two hormones that suppress appetite.
Nutritional Value of Pine Nuts
Dried pine nuts are 2.2% water, 13% carbohydrates, 14% protein, and 68% fat. In a 100-gram reference serving, dried pine nuts supply 673 kcal of food energy and are a rich source of numerous micronutrients, particularly manganese (419% of DV), phosphorus (82% of DV), magnesium (71% of DV), zinc (67% of DV), copper (65% of DV), vitamin E (62% of DV), vitamin K (51% of DV), and the B vitamins, thiamin and niacin (29–35% of DV).
One ounce of dried pine nuts provides 178 calories, 5.5 g carbohydrate, 3.3 g protein, 17.3 g fat, 3 g dietary fiber, 8 IU vitamin A, 1.2 mg niacin, 16 mcg folic acid, 178 mg potassium, 20 mg sodium, 10 mg phosphorus, 2 mg calcium, 66 mg magnesium, 1.21 mg zinc, and 1.23 mg manganese.
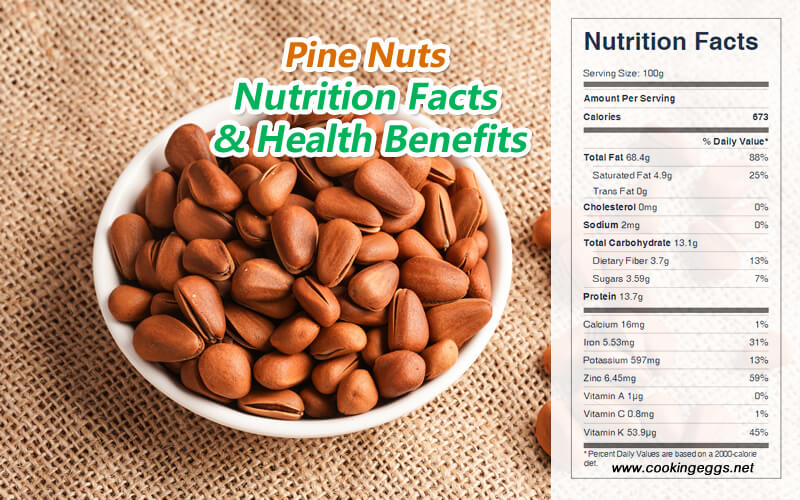
Pine nuts Nutrition Facts Label
Health Benefits of Pine nuts
Pine nuts are especially rich in monounsaturated fatty acids like oleic acid, which help to lower LDL and increase HDL in the blood. Monounsaturated fatty acids in the diet can help to prevent coronary artery disease and strokes by favoring a healthy blood lipid profile.
Like almonds, pine nuts are an excellent source of vitamin E (62% of the Daily Value). Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen species. It is a group of eight fat-soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Studies suggested that people who consumed foods with more vitamin E, or who chose on their own to consume a vitamin E dietary supplement, had a lower incidence of cardiovascular diseases, cancer, dementia, and other diseases.
Pine nuts are an excellent source of the vitamin B complex group, such as thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, folate, choline, and vitamin B6. Vitamin B is an essential nutrient for the body, as coenzymes and sugars participate in the metabolism of proteins and fats in the body. It can maintain the health of the body and is a very important factor in the prevention and treatment of many diseases.
Pine nuts are rich in vitamin K. The human body requires vitamin K for post-synthesis modification of certain proteins that are required for blood coagulation or for controlling the binding of calcium in bones and other tissues. Research suggests that deficiency of vitamin K may also weaken bones, potentially contributing to osteoporosis, and may promote calcification of arteries and other soft tissues.
In addition, pine nuts contain small amounts of essential minerals like manganese, phosphorus, magnesium, copper, iron, zinc, potassium, and selenium. They are one of the richest sources of manganese. Manganese is an all-important co-factor for the antioxidant enzyme, superoxide dismutase. Therefore, consumption of pine kernels helps the human body develop resistance against infectious agents and scavenge harmful oxygen-free radicals.